Precipitation: variability and extreme event
As it was shown above, their exists several devices to measure the rainfall. Due to the extreme variability of the rainfall intensity and the duration of the events, the classical approaches fail to characterize the probability of the rainfall.
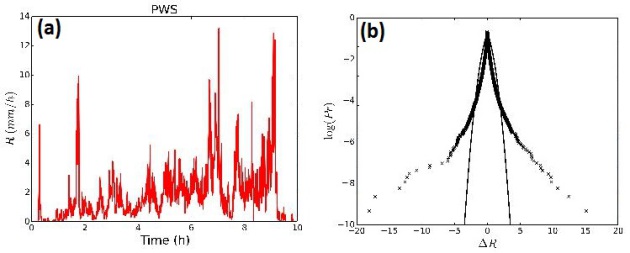
The increment of the rain rate shows an extreme values that the classical (Gaussian) distribution does not reproduce. In fact, rainfall has a very strong heterogeneity on a wide range of spatial and temporal scales. The classical method of analysis are therefore obliged to introduce scale truncation and ad hoc parameterization, causing a loss of information on some ranges of scales. The impacts of extreme value of precipitation on hydrological systems, especially in the urban environment could cause serious disasters
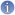 Information[1]
Information[1]




