Precipitation : measurement
Rain gauges:
The rain gauges are widely used to measure the precipitation, because they are not expensive and they provide a direct and robust rainfall measurement.
 Information[1]
Information[1]The measurement principle of a tipping bucket rain gauge consists on collecting precipitation that falls into the funnel and directs it to one of the two small compartments below that can collect water in turn thanks to a pivoting bucket system. The principal inconvenient of the rain gauges is that they represent a very limited space.
Disdrometer: Disdromètre , is an instrument used in meteorology to measure the diameter distribution of hydrometeors and their fall speed . The diameter distribution and number of particles of each diameter to calculate the rate of rainfall which helps in the calibration of remote sensing devices such as weather radar. The falling speed is connected , in turn , to the precipitation stage |  |
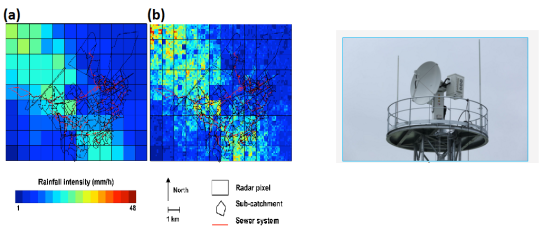
Weather radars:
Weather radars characterize the precipitation over a large surface. They do not measure the precipitation directly, but the reflection by precipitation echoes of the transmitted signal.