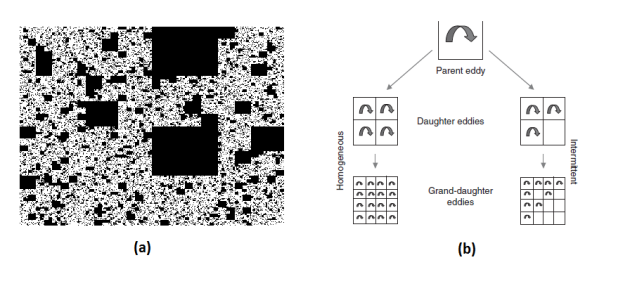
β-model
The simplest cascade model is the
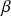 -model ([Novikov, E. A., & Stewart, R. W. 1964][1], [Frisch, U et al, 1978][2]). This model takes into account the intermittency of the studied field by assigning two possible states, than the generated structures can be
-model ([Novikov, E. A., & Stewart, R. W. 1964][1], [Frisch, U et al, 1978][2]). This model takes into account the intermittency of the studied field by assigning two possible states, than the generated structures can be "alive"
or "dead"
. The random variable
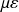 follow a binomial law as :
follow a binomial law as :
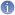 Information[3]
Information[3]The
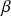 -model is very caricatural of some physical process, However, it is an excellent pedagogical case to introduce de cascade phenomenology.
-model is very caricatural of some physical process, However, it is an excellent pedagogical case to introduce de cascade phenomenology.