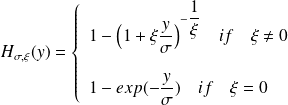Conditional distribution of the excesses
The second part of EVT is called the POT method (Peak Over Threshold) consists to use the observations that exceed a certain deterministic threshold and especially the differences between the observations and the threshold, called excess.
Let
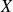 a random variable with a CDF
a random variable with a CDF
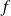 and
and
 which is a real enough large, called threshold. We define the excess over the threshold
which is a real enough large, called threshold. We define the excess over the threshold
 the set of random variables
the set of random variables
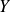 such as:
such as:
We look from the distribution
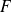 of
of
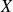 to define a conditional distribution
to define a conditional distribution
 with respect to
with respect to
 for the random variable exceeding the threshold. We can define the conditional distribution of the excess such as:
for the random variable exceeding the threshold. We can define the conditional distribution of the excess such as:
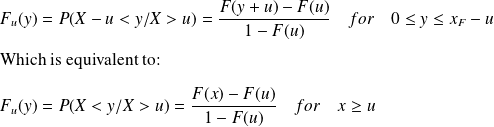
This method allows to determine by which PDF that we can fit the conditional distribution of excesses
 when the threshold tends to the point
when the threshold tends to the point
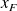 .
.
Lets
 the conditional distribution of cumulative distribution function
the conditional distribution of cumulative distribution function
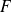 with respect to a threshold
with respect to a threshold
 . When the threshold
. When the threshold
 tends to the value
tends to the value
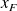 :
:
The conditional distribution converges to the function
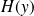 which corresponds to the Generalized Pareto cumulative distribution noted GPD. Generalized Pareto law is written as:
which corresponds to the Generalized Pareto cumulative distribution noted GPD. Generalized Pareto law is written as:
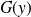 corresponds to Generalized Extreme Value law. For
corresponds to Generalized Extreme Value law. For
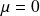 (location parameter) the GPD law can be written as:
(location parameter) the GPD law can be written as: