Coin tossing example
Let's start with a simple example: which is the distribution of N flips of coin tossing, we assign the value 0 for the heads and the value 1 for the tails.
Lets
 the value of one flip, we have
the value of one flip, we have
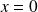 with the probability
with the probability
 and
and
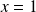 with the probability of
with the probability of
 . The random variable
. The random variable
 has the average
has the average
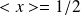 and a standard deviation
and a standard deviation
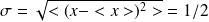 .
.
It is easy to show that the partial average
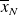 of
of
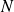 independent flips of
independent flips of
 with
with
 :
:
admit a Gaussian distribution:
The central limit theorem can provide more detailed information about the behavior of
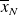 However, the approximation by the central limit theorem may not be accurate if
However, the approximation by the central limit theorem may not be accurate if
 is far from
is far from
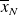 . Also, it does not provide information about the convergence of the tail probabilities as
. Also, it does not provide information about the convergence of the tail probabilities as
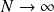 . However, the large deviation theory can provide answers for such problems:
. However, the large deviation theory can provide answers for such problems:
This expression can be deduced from Stirling formula for
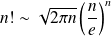 .
.





